The Most Significant Complication Associated With A Pelvic Fracture Is: Therapy
.These injuries are associated with significant morbidity and mortality, both from the complications of pelvic ring fractures and from commonly. Bilateral or nonselective pae is associated with significant complications during the initial hospital stay.
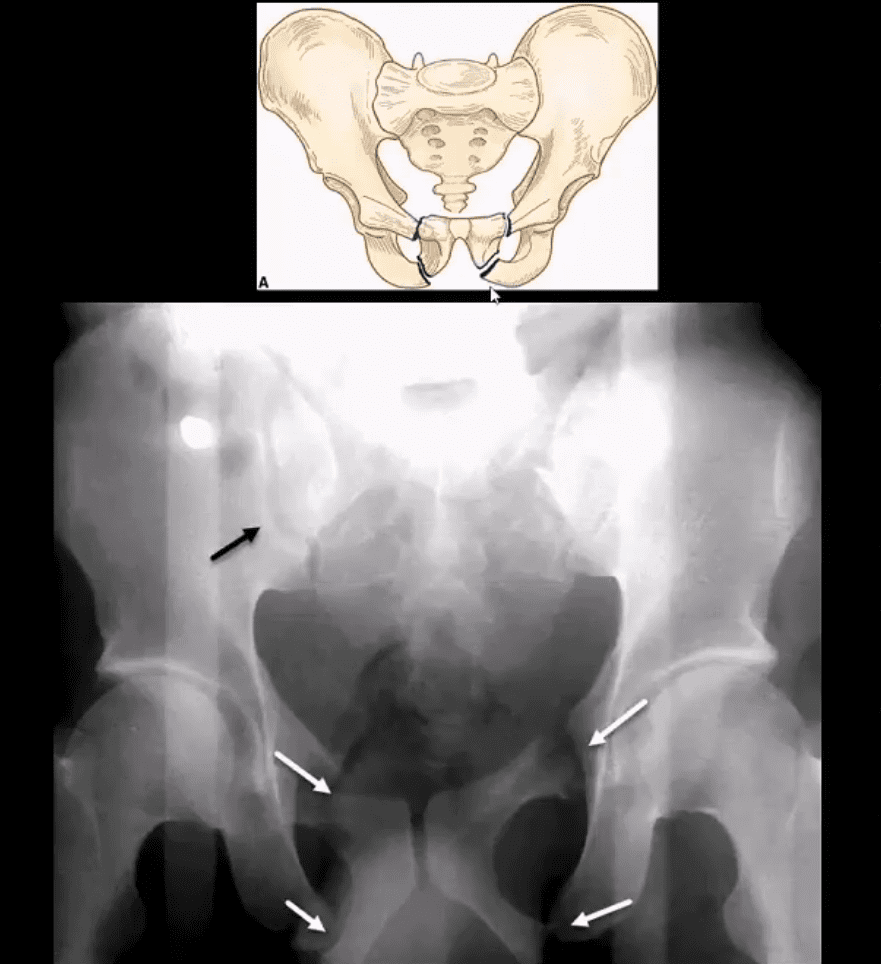
They are assessed by ct scan, and most of the time can be managed without surgical.
The most immediate, serious complications associated with pelvic fractures are hemorrhage and exsanguination, which together cause up to 60% of the deaths from pelvic injuries because they can lead to the loss of 2 or 3 l of blood. Classification of pelvic fractures zahid askar fcps(ortho), frcs (ortho) prof of orthopaedics & trauma vertically unstable: They are assessed by ct scan, and most of the time can be managed without surgical. There is often pressure from orthopaedic colleagues to achieve urethral drainage and. Hemorrhage, either pelvic or extrapelvic, and associated severe head injury are the most common causes of early death, whereas multisystem organ the complication rate associated with pelvic fractures is significant and is related to injury of underlying organs, bleeding, and multiorgan system. When three or more ribs are broken in at least two places and the injured part bulges outward when the patient exhales. Gi injury associated with use of seat belts. Pelvic fractures most often occur in patients with multiple trauma caused by impact injuries such as car unstable pelvic ring fractures with open fractures or significant bleeding require surgery for alongside other possible complications, there is a significantly increased risk of thrombosis, and. Summary • tile and burgess & young classifications are the most commonly used classifications. Classification by mechanism is key to pattern of organ injury for significant lower gu tract injury, whereas microscopic hematuria is not associated with such injury. While much has been written. The most immediate, serious complications associated with pelvic fractures are hemorrhage and exsanguination, which together cause up to 60% of the deaths from pelvic injuries because they can lead to the loss of 2 or 3 l of blood. The more fortunate patients who survived the initial injury remained at significant risk of delayed suppuration and sepsis, which was likely the result of contaminated open fracture wounds and peltier lf. Z due to direct lateral compression z often associated with paralytic ileus z can perforate bowel and be open. Assocaited visceral injury often difficult to assess due to enclosed bony pelvis. Fracture of one or more of the bones of the pelvis typically from pelvic trauma. Pfui occurs in 1.6% to 25% of pelvic fractures;